Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMI6HUW)
| Drug Name |
Terbinafine
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Bramazil; Lamasil; TerbiFoam; Terbina; Lamisil AT; Lamisil Tablet; Ternbinafine HCl; Lamasil (TN); Lamisil (TN); SF 86-327; Terbisil (TN); Zabel (TN); SF-86-327; Terbinafine (USAN/INN); Terbinafine [USAN:BAN:INN]; Lamisil, Terbinex, Corbinal, Zabel, Terbinafine; Terbinafine, SF-86-327, Lamisil, TBNF; (2E)-N,6,6-trimethyl-N-(1-naphthylmethyl)-2-hepten-4-yn-1-amine; (2E)-N,6,6-trimethyl-N-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine; (E)-N,6,6-trimethyl-N-(naphthalen-1-ylmethyl)hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine; (E)-N-(6,6-Dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalene methanamine; (E)-N-(6,6-Dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine; (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-heptenynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenementhamin hydrochloride
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antifungal Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Fungi
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
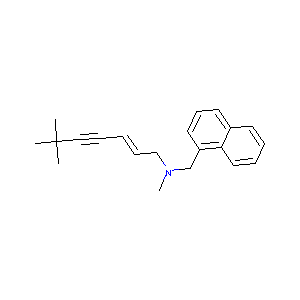 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 1 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 291.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 5.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Terbinafine
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Terbinafine (Comorbidity)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Safety and tolerability of oral antifungal agents in the treatment of fungal nail disease: a proven reality. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2005 Dec;1(4):299-306. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Terbinafine FDA Label | ||||
| 3 | Clinical pipeline report, company report or official report of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) | ||||
| 4 | FDA Approved Drug Products: Lamisil Terbinafine Hydrochloride Oral Tablets | ||||
| 5 | BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs | ||||
| 6 | Darkes MJ, Scott LJ, Goa KL: Terbinafine: a review of its use in onychomycosis in adults. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2003;4(1):39-65. | ||||
| 7 | Baladi MG, Forster MJ, Gatch MB, Mailman RB, Hyman DL, Carter LP, Janowsky A: Characterization of the Neurochemical and Behavioral Effects of Solriamfetol (JZP-110), a Selective Dopamine and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Aug;366(2):367-376. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.248120. Epub 2018 Jun 11. | ||||
| 8 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 9 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 10 | Substrates, inducers, inhibitors and structure-activity relationships of human Cytochrome P450 2C9 and implications in drug development. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(27):3480-675. | ||||
| 11 | Multiple cytochrome P-450s involved in the metabolism of terbinafine suggest a limited potential for drug-drug interactions. Drug Metab Dispos. 1999 Sep;27(9):1029-38. | ||||
| 12 | Terbinafine inhibits endothelial cell migration through suppression of the Rho-mediated pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006 Dec;5(12):3130-8. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0457. | ||||
| 13 | Association of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 inhibition in in vitro assays with drug-induced liver injury. J Toxicol Sci. 2021;46(4):167-176. doi: 10.2131/jts.46.167. | ||||
| 14 | A metoprolol-terbinafine combination induced bradycardia. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2015 Sep;40(3):295-9. | ||||
| 15 | Development of a strategy to identify and evaluate direct and indirect activators of constitutive androstane receptor in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 Dec;170:113510. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.113510. Epub 2022 Nov 8. | ||||
| 16 | Association of Liver Injury From Specific Drugs, or Groups of?Drugs, With Polymorphisms in HLA and Other Genes in a?Genome-Wide Association Study. Gastroenterology. 2017 Apr;152(5):1078-1089. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.016. Epub 2016 Dec 30. | ||||
| 17 | Anti-mycotics suppress interleukin-4 and interleukin-5 production in anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28-stimulated T cells from patients with atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Dec;117(6):1635-46. doi: 10.1046/j.0022-202x.2001.01566.x. | ||||
| 18 | Terbinafine stimulates the pro-inflammatory responses in human monocytic THP-1 cells through an ERK signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2010 Oct 23;87(17-18):537-44. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.08.010. Epub 2010 Sep 9. | ||||
| 19 | Canadian Pharmacists Association. | ||||
| 20 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 21 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 22 | Product Information. Olinvyk (oliceridine). Trevena Inc, Chesterbrook, PA. | ||||
| 23 | Product Information. Sirturo (bedaquiline). Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Titusville, NJ. | ||||
| 24 | AbdelRahman SM, Gotschall RR, Kauffman RE, Leeder JS, Kearns GL "Investigation of terbinafine as a CYP2D6 inhibitor in vivo." Clin Pharmacol Ther 65 (1999): 465-72. [PMID: 10340911] | ||||
| 25 | Product Information. Turalio (pexidartinib). Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., Parsippany, NJ. | ||||
| 26 | Product Information. Piqray (alpelisib). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. Brintellix (vortioxetine). Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Lincolnshire, IL. | ||||
| 28 | Product Information. Ingrezza (valbenazine). Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA. | ||||
| 29 | Brynne N, Svanstrom C, AbergWistedt A, Hallen B, Bertilsson L "Fluoxetine inhibits the metabolism of tolterodin-pharmacokinetic implications and proposed clinical relevance." Br J Clin Pharmacol 48 (1999): 553-63. [PMID: 10583026] | ||||
| 30 | Product Information. Lamisil (terbinafine). Sandoz Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin). Seattle Genetics Inc, Bothell, WA. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Kynamro (mipomersen). Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Juxtapid (lomitapide). Aegerion Pharmaceuticals Inc, Cambridge, MA. | ||||
| 34 | Al-Nawakil C, Willems L, Mauprivez C, et.al "Successful treatment of l-asparaginase-induced severe acute hepatotoxicity using mitochondrial cofactors." Leuk Lymphoma 55 (2014): 1670-4. [PMID: 24090500] | ||||
| 35 | Product Information. Zydelig (idelalisib). Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. | ||||
| 36 | Product Information. Xeglyze (abametapir topical). Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ. | ||||
| 37 | Product Information. Fycompa (perampanel). Eisai Inc, Teaneck, NJ. | ||||
| 38 | Benoist G, van Oort I, et al "Drug-drug interaction potential in men treated with enzalutamide: Mind the gap." Br J Clin Pharmacol 0 (2017): epub. [PMID: 28881501] | ||||
| 39 | Product Information. Abilify (aripiprazole). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 40 | DSouza DL, Levasseur LM, Nezamis J, Robbins DK, Simms L, Koch KM "Effect of alosetron on the pharmacokinetics of alprazolam." J Clin Pharmacol 41 (2001): 452-4. [PMID: 11304902] | ||||
| 41 | Product Information. Tavalisse (fostamatinib). Rigel Pharmaceuticals, South San Francisco, CA. | ||||
